Dr Christian Soeller & Ray Gilbert
Department of Physiology
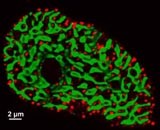
Image now published in: Christian Soeller, David Crossman, Ray Gilbert and Mark B. Cannell, Analysis of ryanodine receptor clusters in rat and human cardiac myocytes, PNAS, September 18, 2007, 104; (38), 14958-14963.
Cross-section through an isolated rat ventricular cardiomyocyte, stained for both alpha actinin (green) and RyR2 receptor (red). The green patches correspond to bundles of contractile machinery and the red puncta represent clusters of ryanodine receptors that release calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum upon activation. Cells were orientated end on using a novel agar embedding method, allowing unprecedented resolution in cross section (~250 nm), that is largely unaffected by the blurring artefacts normally resulting from the limited Z resolution of confocal microscopy. Note the arrangement of release clusters around the contractile machinery which is activated by the calcium rapidly diffusing from the site of release.
Image captured on a Zeiss LSM410 confocal microscope in the Physiology Dept. FMHS and processed using custom written deconvolution software.
Sample preparation and imaging: Ray Gilbert
Data processing and display: Christian Soeller
Funding: Auckland Medical Research Foundation